How much nitrogen can cover crops replace?
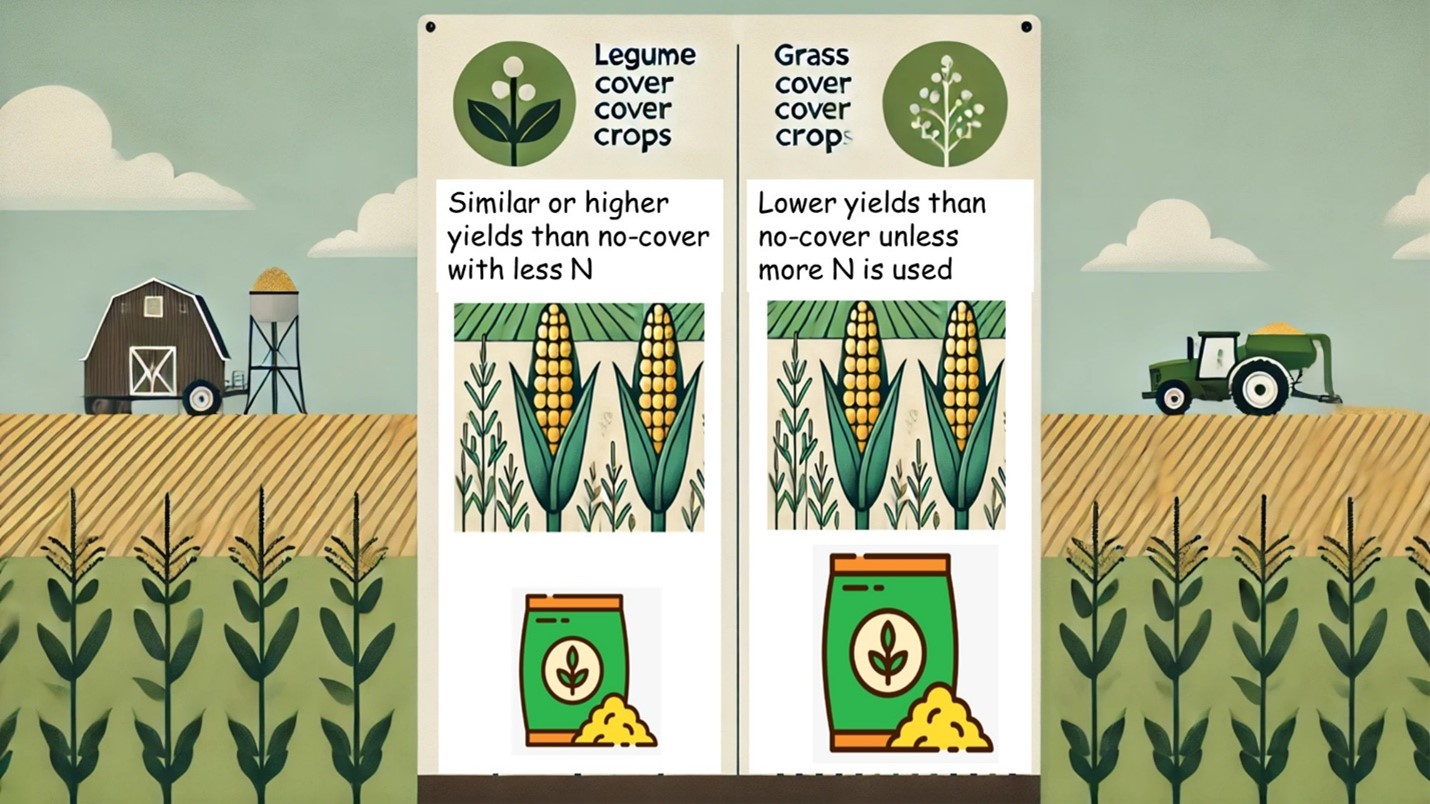
Cover crops provide significant soil benefits when planted after or alongside corn. They can either add nitrogen (N) to the soil or remove it, thereby influencing the N requirements of the subsequent corn crop. Therefore, quantifying the N supplied or removed by cover crops is crucial for determining the appropriate amount of fertilizer needed to achieve comparable corn yields as those without cover crops.
To address this, scientists from West Texas A&M University, Tennessee State University, USDA-Beltsville Research Center, and the University of Illinois statistically analyzed multi-state yield data from experiments across the United States, comparing corn fertilized with and without cover crops. The study found that legume cover crops resulted in similar or higher corn yields with less fertilizer compared with no cover crops. Conversely, grass cover crops led to lower corn yields unless additional fertilizer was applied.
These findings shed new light on the role of cover crops in N management within corn systems. Understanding the extent to which cover crops can replace fertilizer inputs can inform better field management practices and policy regulations aimed at promoting sustainable corn production.
Dig deeper
Marcillo, G. S., Thapa, R., Mirsky, S. B., & Martin, N. (2024). The nitrogen value of cover crops: How much N can cover crops replace? Agricultural & Environmental Letters, 9, e70006. https://doi.org/10.1002/ael2.70006
Text © . The authors. CC BY-NC-ND 4.0. Except where otherwise noted, images are subject to copyright. Any reuse without express permission from the copyright owner is prohibited.







